VB.NET InStr() – Code Sample
Posted by asp.net videos on Monday, February 7, 2011 · Leave a Comment
VB.NET InStr Example – Code Sample Syntax
Abstract: – Illustrates using VB.NET InStr Code Example.
*** 2. InStr Syntax ***
Purpose:
Returns an integer that represents the position of the first occurrence of
the second string in the first string. The search starts at the specified
position in the string. If the string is not found, the result is 0
Syntax:
InStr(startIndex, stringToSearch, stringToFind)
| Parameters |
Description |
startIndex |
Optional. specifies where to start looking. Zero-based.
|
| stringToSearch |
Required – string that you want to search
|
| stringToFind |
Required – string that you are trying to
find into parameter2
|
| Result Data Type |
Description |
string |
Returns a (zero-based) integer that represents the
position of the first occurrence of the second string in the first
string. The search starts at the specified position in the string.
If the string is not found, the result is 0
|
*** 3. InStr – Quick Example ***
|
Dim strField1 As String = ” This “
Dim strField2 As String = “is”
Console.WriteLine(InStr(1, strField1, strField2)) ‘Returns 4 – spaces are counted
|
*** 4. InStr – Full Example ***
InStr Example Output Screenshot
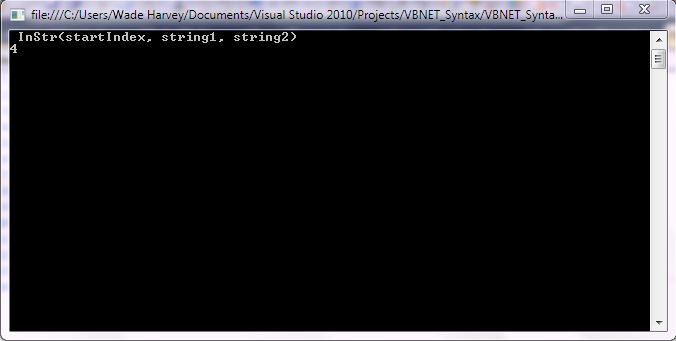
Step 1: Click Visual Basic to Cut-n-paste code into clsInStr.vb
Public Class clsInStr
Public Sub Main()
'****************************************************************************************
' Purpose: Returns an integer that represents the position of the first occurrence of
' the second string in the first string. The search starts at the specified
' position in the string. If the string is not found, the result is 0
'
' Syntax: InStr(startIndex, stringToSearch, stringToFind)
'
' Parameter1: startIndex - Optional. specifies where to start looking. Zero-based.
'
' Parameter2: stringToSearch - Required - string that you want to search
'
' Parameter3: stringToFind - Required - string that you are trying to
' find into parameter2
'
' Result: string - Returns a (zero-based) integer that represents the
' position of the first occurrence of the second string in the first
' string. The search starts at the specified position in the string.
' If the string is not found, the result is 0
'
' Quick Example: Dim strField1 As String = " This "
' Dim strField2 As String = "is"
' Console.WriteLine(InStr(1, strField1, strField2)) 'Returns 4 - spaces are counted
'
'****************************************************************************************
Console.WriteLine(" InStr(startIndex, string1, string2)")
Dim strField1 As String = " This "
Dim strField2 As String = "is"
Console.WriteLine(InStr(1, strField1, strField2)) 'Returns 4 - spaces are counted
'write blank line to make output easier to read
Console.WriteLine()
'Prevent console from closing before you press enter
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Class |
Public Class clsInStr
Public Sub Main()
'****************************************************************************************
' Purpose: Returns an integer that represents the position of the first occurrence of
' the second string in the first string. The search starts at the specified
' position in the string. If the string is not found, the result is 0
'
' Syntax: InStr(startIndex, stringToSearch, stringToFind)
'
' Parameter1: startIndex - Optional. specifies where to start looking. Zero-based.
'
' Parameter2: stringToSearch - Required - string that you want to search
'
' Parameter3: stringToFind - Required - string that you are trying to
' find into parameter2
'
' Result: string - Returns a (zero-based) integer that represents the
' position of the first occurrence of the second string in the first
' string. The search starts at the specified position in the string.
' If the string is not found, the result is 0
'
' Quick Example: Dim strField1 As String = " This "
' Dim strField2 As String = "is"
' Console.WriteLine(InStr(1, strField1, strField2)) 'Returns 4 - spaces are counted
'
'****************************************************************************************
Console.WriteLine(" InStr(startIndex, string1, string2)")
Dim strField1 As String = " This "
Dim strField2 As String = "is"
Console.WriteLine(InStr(1, strField1, strField2)) 'Returns 4 - spaces are counted
'write blank line to make output easier to read
Console.WriteLine()
'Prevent console from closing before you press enter
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Class Step 2: Click Visual Basic to Cut-n-paste code into Module1.vb
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim myclsInStr As New clsInStr
myclsInStr.Main()
End Sub
End Module |
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim myclsInStr As New clsInStr
myclsInStr.Main()
End Sub
End Module Prerequistes:
- Install Visual Basic (Express or Standard Edition)
- Install SQL Server Express
- Download Northwind and pubs Database
- Attach Northwind Database to Databases in Sql Express
- Attach pubs Database to Databases in Sql Express
Notes:
- Console Application is used to simplify things, but Windows Forms or Web Forms could also be used
- You can build a library of syntax examples by using same project over and over and just commenting out what you do not want to execute in Module1.vb
Instructions:
- Use Visual Basic 2010 Express or Standard Edition
- Create new project;
- Click File/New Project
- Select Console Application Template
- Select Visual Basic for Language
- name of project could be VBNET_Syntax.
- Add New folder named “StringManipulation”
- Right-click project name in solution explorer;
- add new folder;
- name of folder could be: StringManipulation
- Add Class Named clsInStr to StringManipulation folder
- Right-click StringManipulation folder;
- add new item;
- Select class
- Class name could be clsInStr
- Click on Visual Basic in code in step 1 above to copy code into clsInStr.vb
- Click on Visual Basic in code in step 2 above to copy code into Module1.vb
- Click green arrow or press F5 to run program
|
 Download Source Code for All VB Console Examples in One Project
Download Source Code for All VB Console Examples in One Project
